What Is The Difference Between Sn1 And Sn2 Reactions
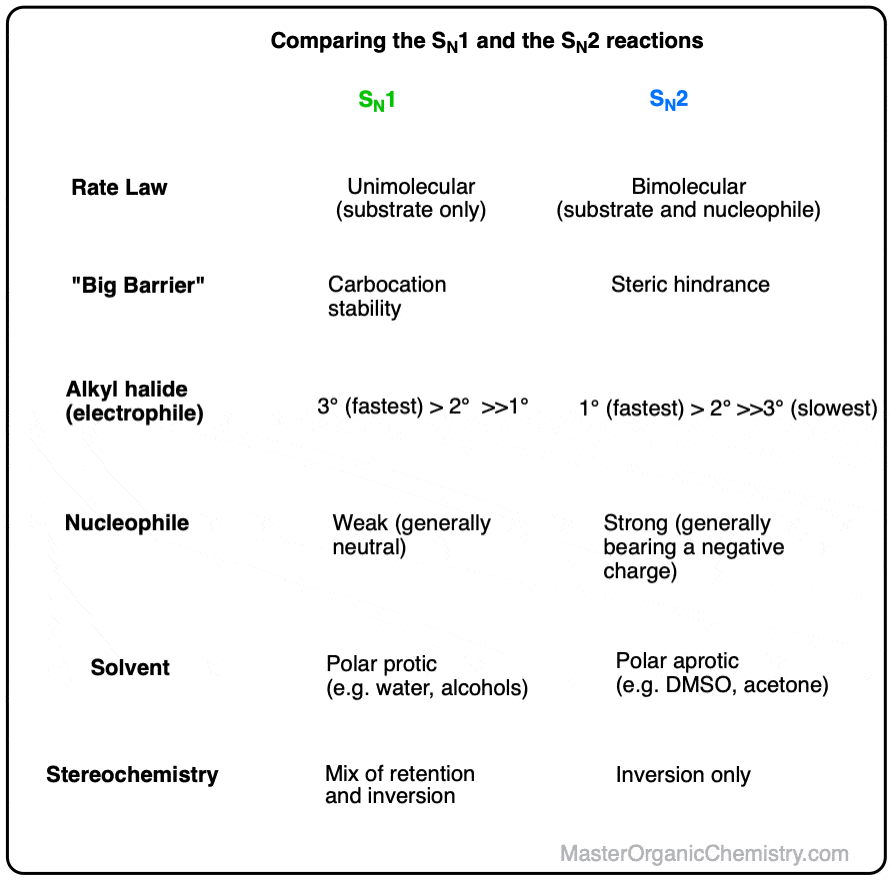
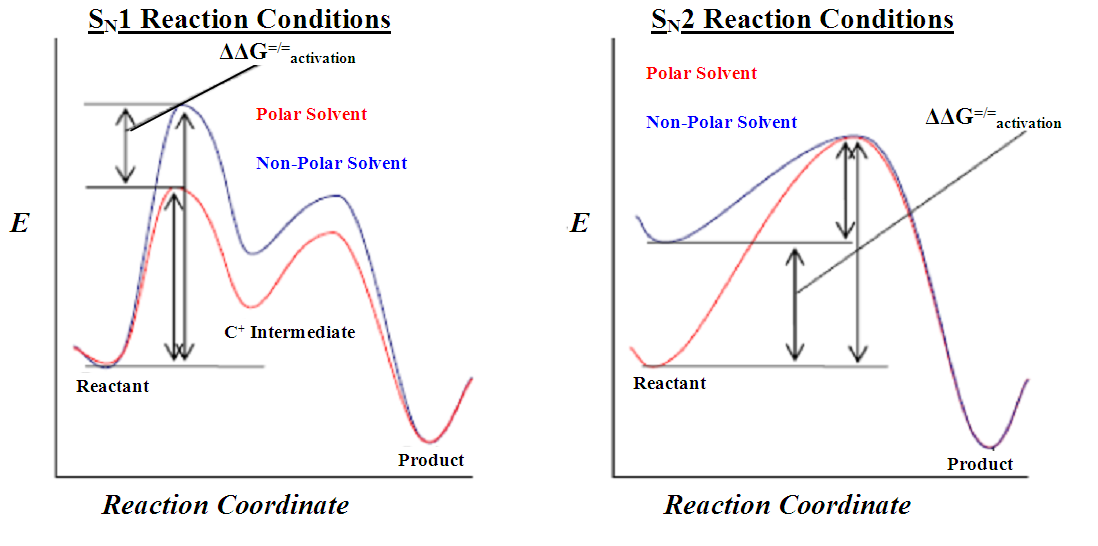
What Is The Difference Between Sn1 And Sn2 Reactions - Sn1 and sn2 are generally confused for being one and the same, however there are certain defining characteristics that separates sn1 from sn2. S n 1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents (h 2 o, roh etc), and usually are solvolysis reactions. Comparison between s n 2 and s n 1 reactions. Considered both as nucleophilic substitution. S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf etc). For example, the reaction below has a tertiary alkyl bromide as the electrophile, a weak nucleophile, and a polar protic solvent (we’ll.
S n 1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents (h 2 o, roh etc), and usually are solvolysis reactions. Comparison between s n 2 and s n 1 reactions. For example, the reaction below has a tertiary alkyl bromide as the electrophile, a weak nucleophile, and a polar protic solvent (we’ll. Considered both as nucleophilic substitution. S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf etc). Sn1 and sn2 are generally confused for being one and the same, however there are certain defining characteristics that separates sn1 from sn2.
For example, the reaction below has a tertiary alkyl bromide as the electrophile, a weak nucleophile, and a polar protic solvent (we’ll. Comparison between s n 2 and s n 1 reactions. Considered both as nucleophilic substitution. S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf etc). Sn1 and sn2 are generally confused for being one and the same, however there are certain defining characteristics that separates sn1 from sn2. S n 1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents (h 2 o, roh etc), and usually are solvolysis reactions.
Difference Between SN1 And SN2 Reactions, Detailed Comparison
S n 1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents (h 2 o, roh etc), and usually are solvolysis reactions. Considered both as nucleophilic substitution. For example, the reaction below has a tertiary alkyl bromide as the electrophile, a weak nucleophile, and a polar protic solvent (we’ll. Sn1 and sn2 are generally confused for being one and the same, however.
Solusi Cerdas Bookshelves Orga brainly.cyou
S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf etc). S n 1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents (h 2 o, roh etc), and usually are solvolysis reactions. For example, the reaction below has a tertiary alkyl bromide as the electrophile, a weak nucleophile, and a polar protic solvent (we’ll. Comparison between s n.
[Solved] What is the difference between an SN1 reaction and an SN2
Sn1 and sn2 are generally confused for being one and the same, however there are certain defining characteristics that separates sn1 from sn2. Considered both as nucleophilic substitution. Comparison between s n 2 and s n 1 reactions. S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf etc). For example, the reaction below has a tertiary.
Difference Between Sn1 And Sn2
S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf etc). Comparison between s n 2 and s n 1 reactions. Sn1 and sn2 are generally confused for being one and the same, however there are certain defining characteristics that separates sn1 from sn2. Considered both as nucleophilic substitution. S n 1 reactions are favored by polar.
Difference Between Sn1 And Sn2 Reaction Slidesharefile
S n 1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents (h 2 o, roh etc), and usually are solvolysis reactions. Sn1 and sn2 are generally confused for being one and the same, however there are certain defining characteristics that separates sn1 from sn2. Considered both as nucleophilic substitution. Comparison between s n 2 and s n 1 reactions. S n.
19. what is the difference between SN1 and SN2 mechanism
S n 1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents (h 2 o, roh etc), and usually are solvolysis reactions. For example, the reaction below has a tertiary alkyl bromide as the electrophile, a weak nucleophile, and a polar protic solvent (we’ll. Considered both as nucleophilic substitution. Comparison between s n 2 and s n 1 reactions. Sn1 and sn2.
Difference Between Sn1 And Sn2
S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf etc). For example, the reaction below has a tertiary alkyl bromide as the electrophile, a weak nucleophile, and a polar protic solvent (we’ll. Sn1 and sn2 are generally confused for being one and the same, however there are certain defining characteristics that separates sn1 from sn2. Comparison.
Difference Between SN1 and SN2 Reactions
For example, the reaction below has a tertiary alkyl bromide as the electrophile, a weak nucleophile, and a polar protic solvent (we’ll. Considered both as nucleophilic substitution. S n 1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents (h 2 o, roh etc), and usually are solvolysis reactions. S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf.
Difference Between SN1 and SN2 Reactions
Comparison between s n 2 and s n 1 reactions. S n 1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents (h 2 o, roh etc), and usually are solvolysis reactions. S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf etc). For example, the reaction below has a tertiary alkyl bromide as the electrophile, a weak nucleophile,.
Difference Between Sn1 And Sn2 Reactions Pdf Images and Photos finder
For example, the reaction below has a tertiary alkyl bromide as the electrophile, a weak nucleophile, and a polar protic solvent (we’ll. Sn1 and sn2 are generally confused for being one and the same, however there are certain defining characteristics that separates sn1 from sn2. S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf etc). Considered.
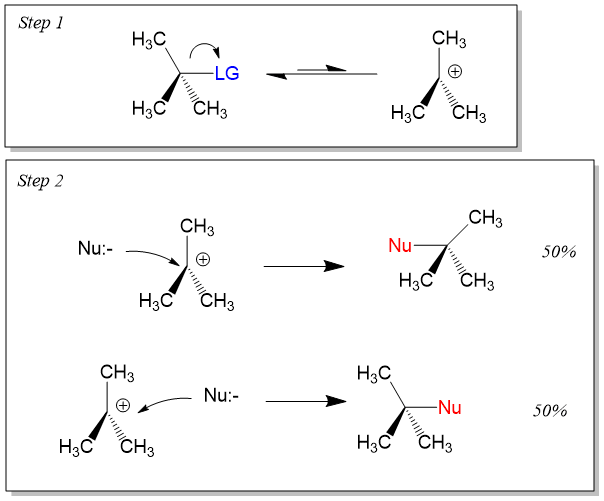
For Example, The Reaction Below Has A Tertiary Alkyl Bromide As The Electrophile, A Weak Nucleophile, And A Polar Protic Solvent (We’ll.
Considered both as nucleophilic substitution. S n 2 reactions are favored by polar aprotic solvents (acetone, dmso, dmf etc). Comparison between s n 2 and s n 1 reactions. S n 1 reactions are favored by polar protic solvents (h 2 o, roh etc), and usually are solvolysis reactions.